|
Strain Name
|
C57BL/6-Ccr8tm1(CCR8)Bcgen/Bcgen
|
Common Name
|
B-hCCR8 mice
|
|
Background
|
C57BL/6
|
Catalog number
|
110096
|
Related Genes
|
C-C motif chemokine receptor 8; CY6; TER1; CCR-8;
CKRL1; CDw198; CMKBR8; GPRCY6; CMKBRL2; CC-CKR-8
|
NCBI Gene ID
|
12776
|
mRNA expression analysis
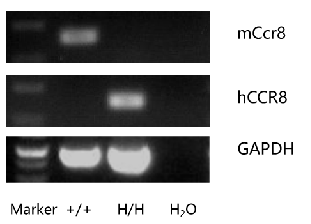
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice by RT-PCR. Mouse Ccr8 mRNA was detectable in thymocytes of wild-type mice (+/+) . Human CCR8 mRNA was detectable only in homozygous B-hCCR8 mice (H/H) but not in wild-type mice (+/+).
Protein expression analysis
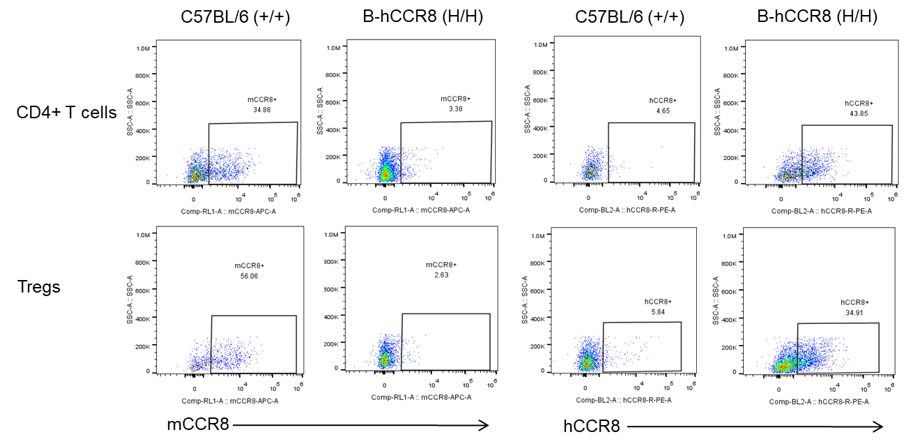
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. MC38 cells were inoculated into wild-type C57BL/6 (+/+) and homozygous B-hCCR8 mice (H/H). Tumors were harvested at the endpoint of experiment, and the TILs were analyzed by flow cytometry. Human CCR8 was both detectable on CD4+ T cells and Treg cells in tumors of homozygous B-hCCR8 mice, and mouse CCR8 was detectable only in wild-type mice.
Leukocytes cell subpopulation and CCR8 expression analysis in spleen, thymus,
and blood of B-hCCR8 mice (non-tumor bearing)
Protein expression analysis of mouse and human CCR8 in spleen
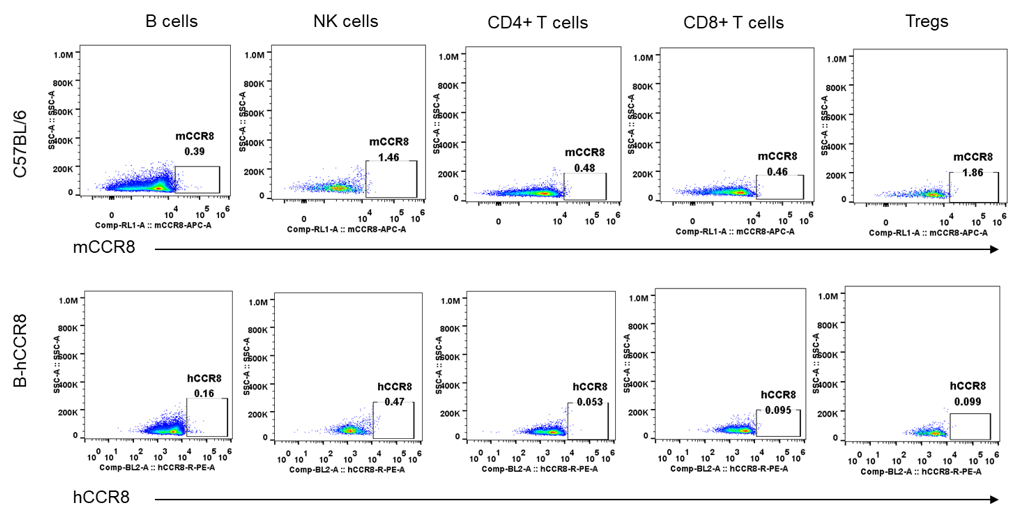
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. Spleen was isolated from the mice, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Human and mouse CCR8 were not expressed neither in splenocytes of wild-type mice nor B-hCCR8 mice separately.
Protein expression analysis of mouse and human CCR8 in thymus
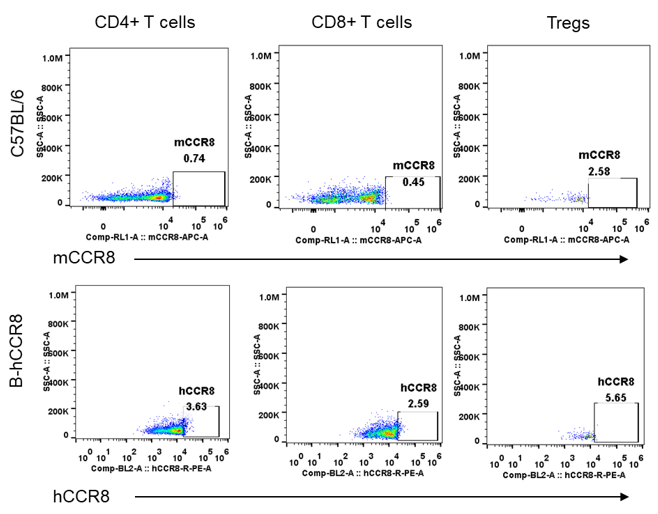
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. Thymus was isolated from the mice, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Human and mouse CCR8 were not expressed neither in thymocytes of wild-type mice nor B-hCCR8 mice separately.
Protein expression analysis of mouse and human CCR8 in blood
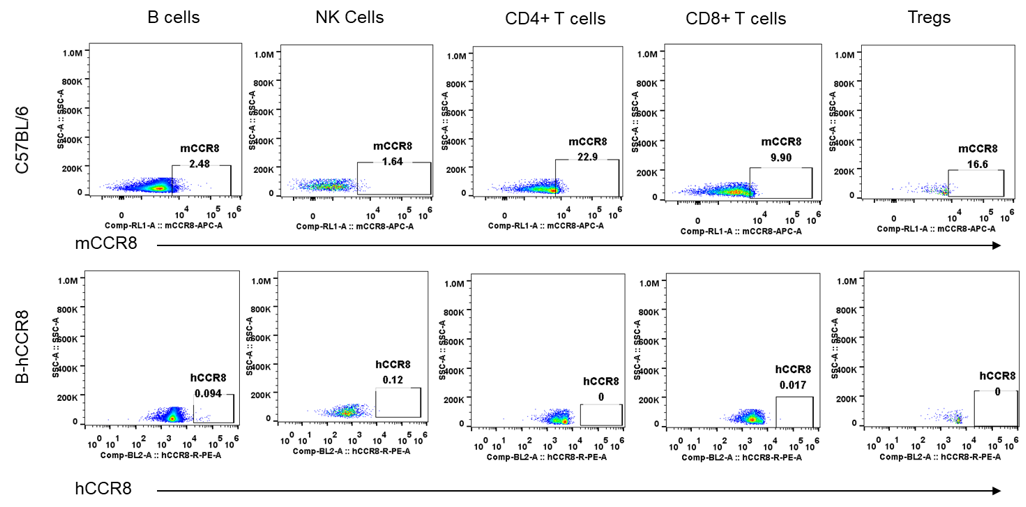
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. Blood were harvested from the mice, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Human and mouse CCR8 were not expressed neither in blood cells of wild-type mice nor B-hCCR8 mice separately.
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in B-hCCR8 mice
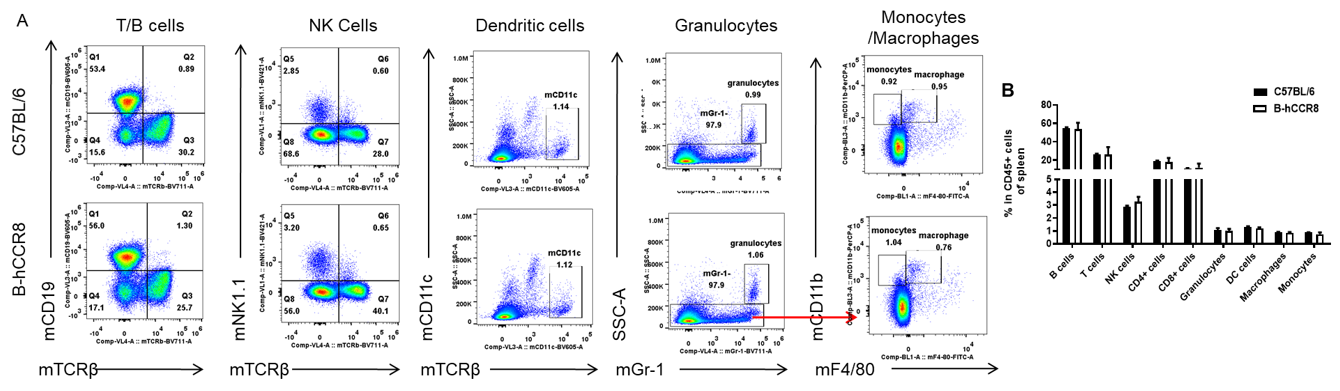
Analysis of spleen leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Splenocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes were performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cell, B cell, NK cell, monocyte, dendritic cell, granulocyte and macrophage in homozygous B-hCCR8 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CCR8 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
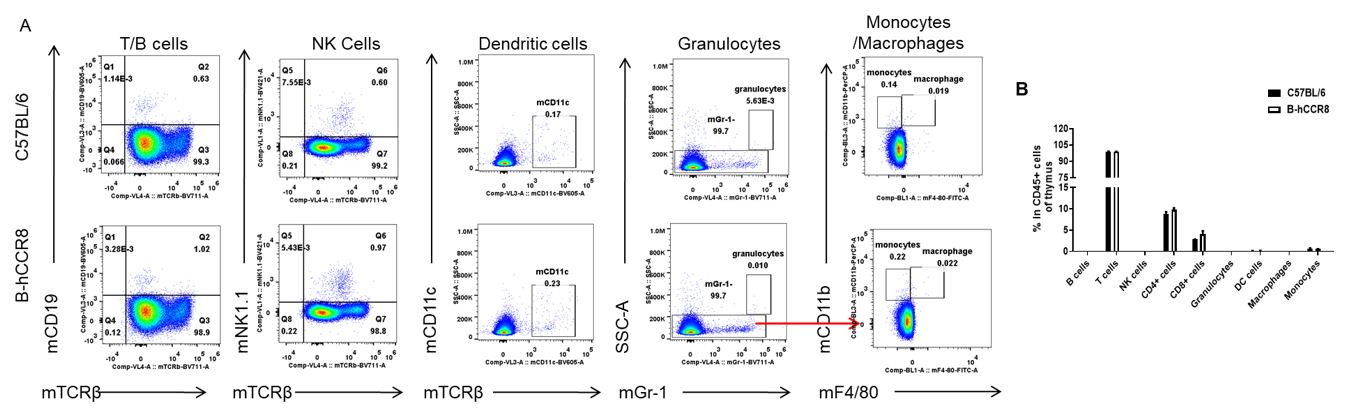
Analysis of thymocytes leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Thymocytes were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the thymocytes were performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cell, B cell, NK cell, monocyte, dendritic cell, granulocyte and macrophage in homozygous B-hCCR8 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CCR8 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in thymus. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
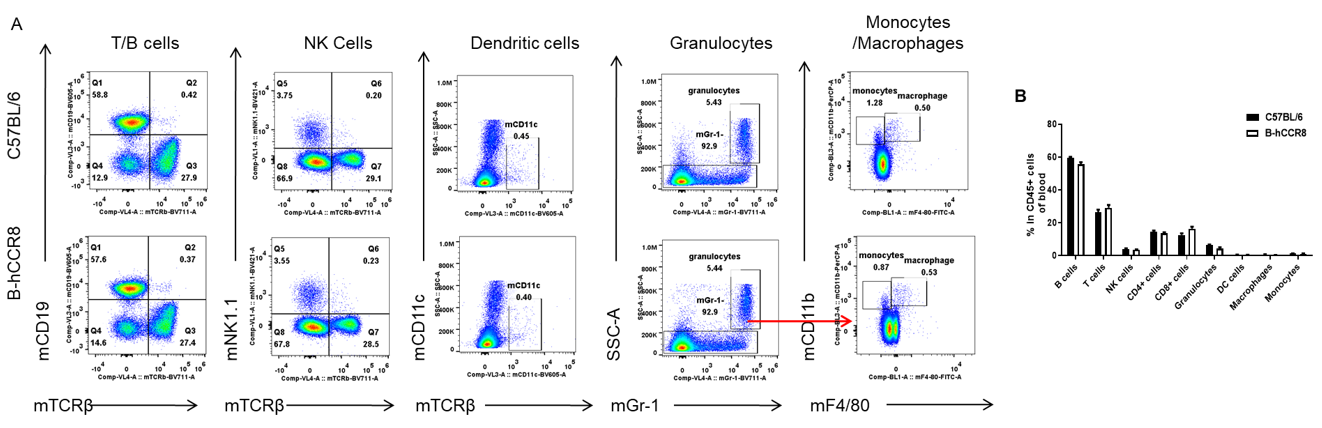
Analysis of blood leukocyte subpopulations by FACS. Blood were isolated from female C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice (n=3, 8-week-old). Flow cytometry analysis of the blood cells were performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. A. Representative FACS plots. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. B. Results of FACS analysis. Percent of T cell, B cell, NK cell, monocyte, dendritic cell, granulocyte and macrophage in homozygous B-hCCR8 mice were similar to those in the C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that CCR8 humanized does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these cell types in blood. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in B-hCCR8 mice
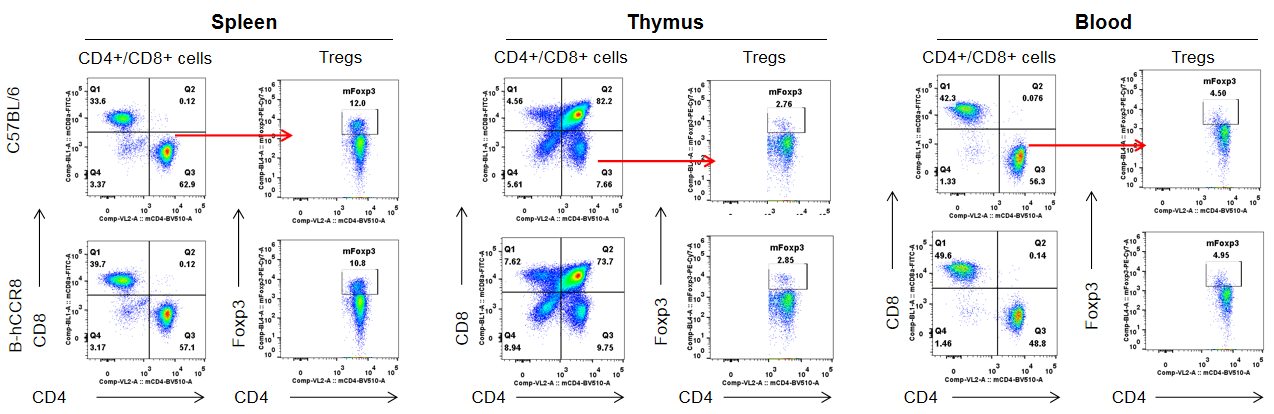
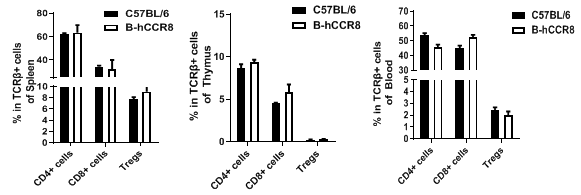
Analysis of T cell subpopulation in spleen, thymus and blood.The lymphocytes were isolated from spleen, thymus and blood in C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice (n=3, 8-week-old). The proportion of T cells subpopulation was tested by flow cytometry. There were no differences between C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice, demonstrating that humanized of CCR8 does not change the overall development, differentiation or distribution of these T cell subtypes. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Establishment of mouse MC38 colon cancer model based on B-hCCR8 mice and analysis leukocyte subpopulations and CCR8 expression of tumor, spleen, and blood.
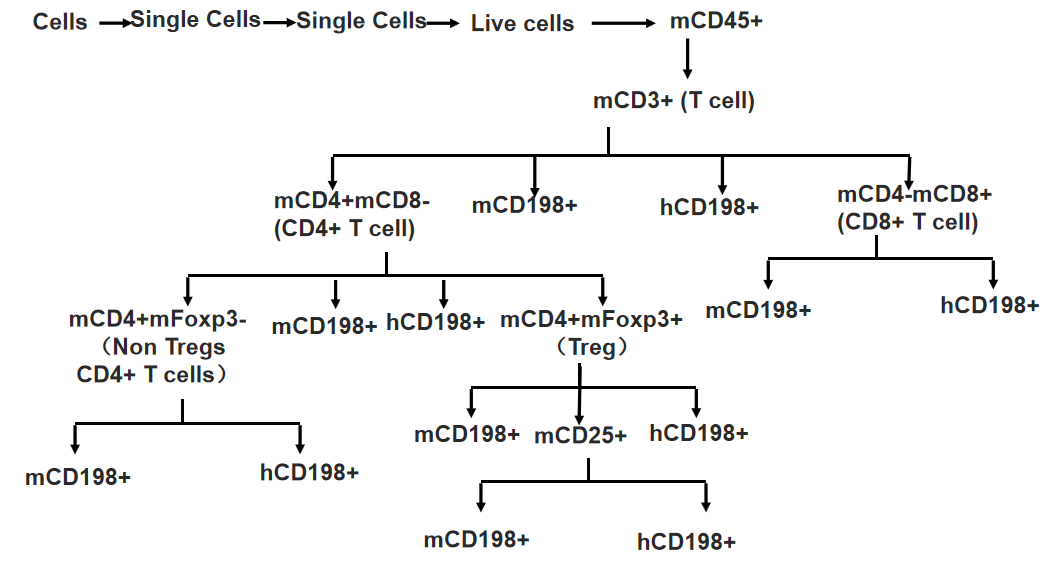
Gating strategy
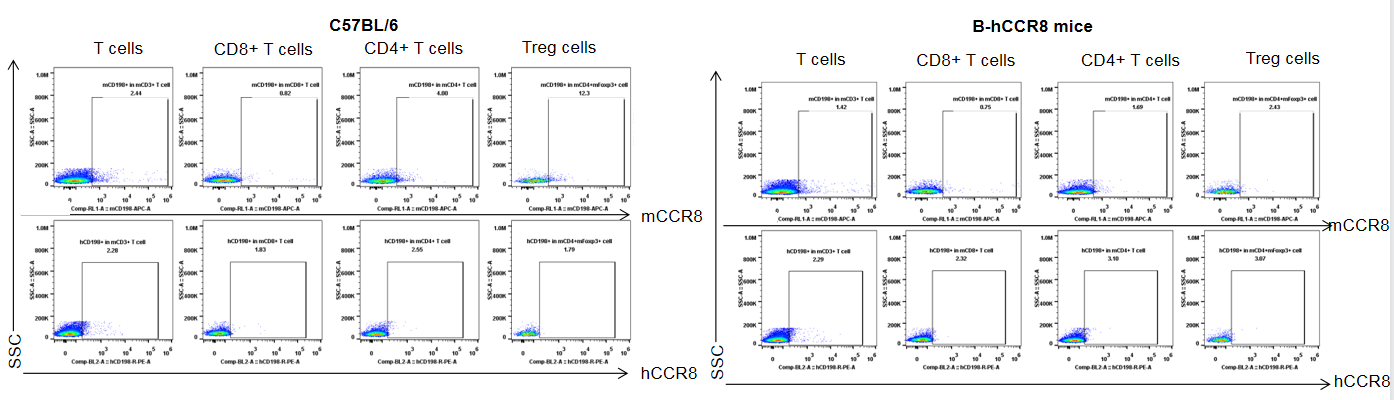
Protein expression analysis of mouse and human CCR8 in tumor
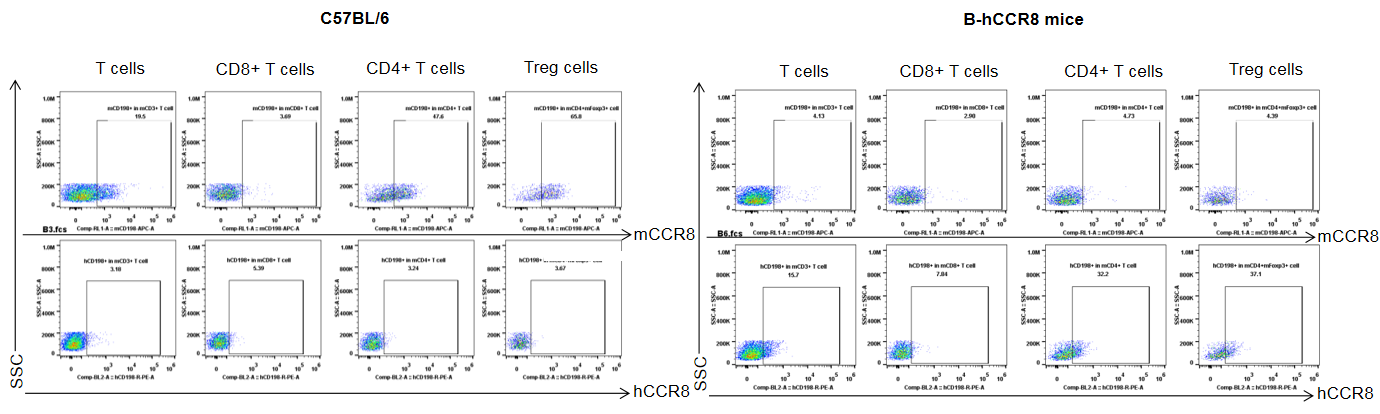
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. TILs were harvested at the endpoint of experiment, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Human CCR8 was both detectable on CD4+ T cells and Treg cells in tumors of homozygous B-hCCR8 mice, and mouse CCR8 was detectable in wild-type mice.
Protein expression analysis of mouse and human CCR8 in spleen
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. Splenocytes were harvested at the endpoint of experiment, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mouse CCR8 was slightly expressed in Treg cells in spleen of wild-type mice, but human CCR8 was not detectable in homozygous B-hCCR8 mice. Because the CCR8 expression was low in the spleen, so maybe the CCR8 expressed much lower in the spleen of homozygous B-hCCR8 mice that we can’t detect it, or the antibody dose we used in this experiment is not saturated.
Protein expression analysis of mouse and human CCR8 in blood
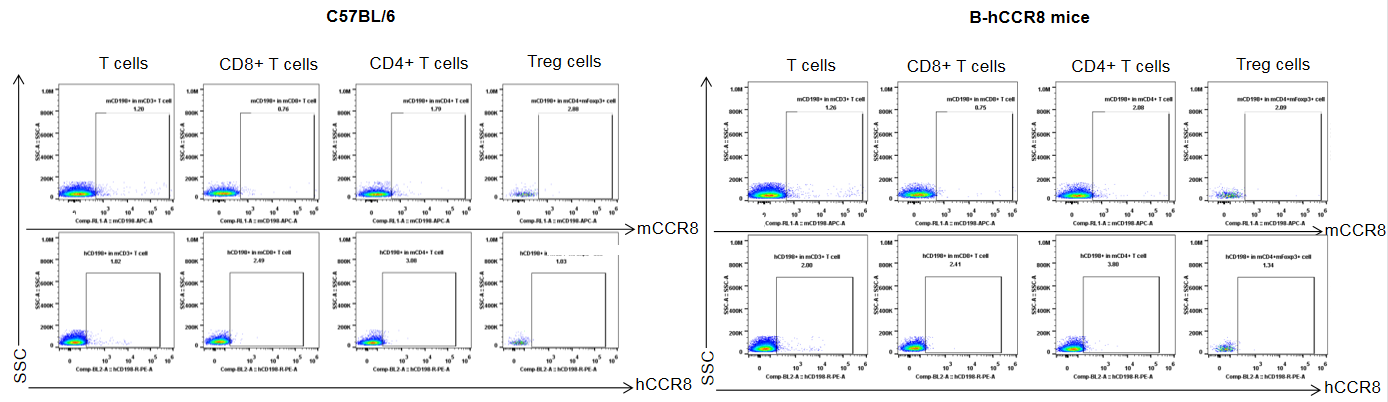
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. Blood cells were harvested at the endpoint of experiment, and analyzed by flow cytometry. Human and mouse CCR8 were not expressed neither in blood cells of wild-type mice nor human CCR8 separately.
Summary for protein expression
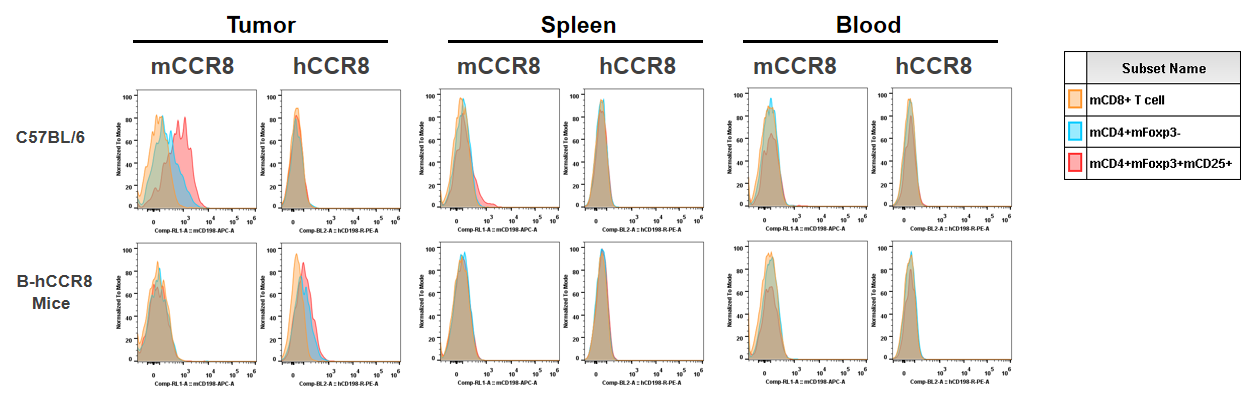
Strain specific analysis of CCR8 gene expression in B-hCCR8 mice by FACS. Human CCR8 was both detectable on CD4+ T cells and Treg cells in tumors of homozygous B-hCCR8 mice, but not in splenocytes and blood cells. Mouse CCR8 was detectable in tumors and slightly expressed in splenocytes of wild-type mice, but not in blood cells.
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in B-hCCR8 mice bearing MC38 tumors
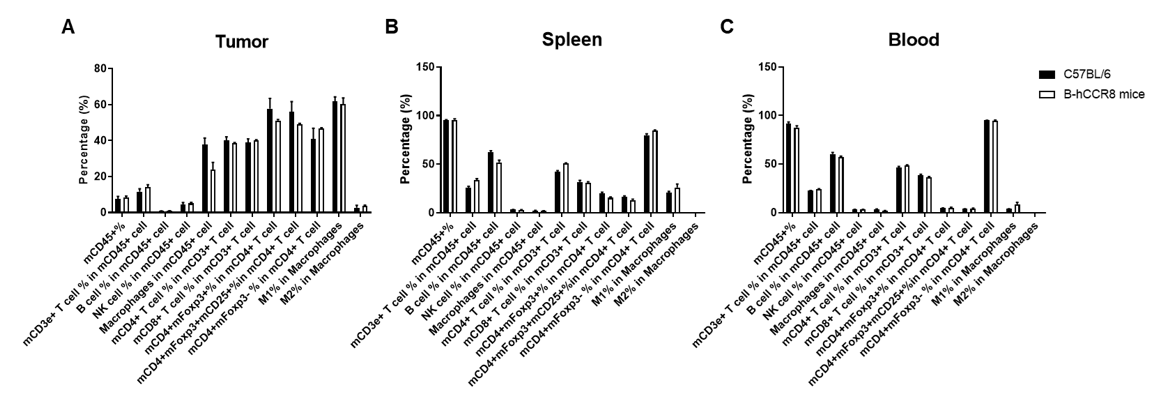
Analysis of leukocyte subpopulations of tumor, spleen and blood by FACS.
Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hCCR8 mice (female, 8 week-old, n=3). Tumors, splenocytes and blood cells were harvested at the endpoint of the experiment (tumor volumes~1000mm3), and flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess leukocyte subpopulations. Single live cells were gated for the CD45+ population and used for further analysis as indicated here. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Complete blood count and blood chemistry
Blood routine test in B-hCCR8 mice
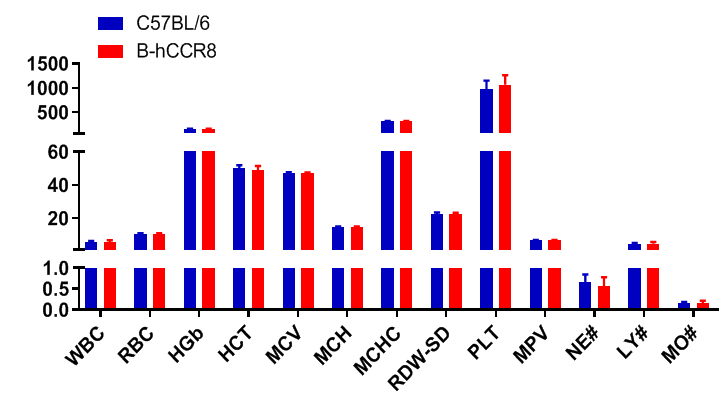
Complete blood count (CBC). Blood from female C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice (n=8, 9 week-old) was collected and analyzed for CBC. The measurements of B-hCCR8 mice were similar to that in C57BL/6 mice, indicating that humanization does not change blood cell composition and morphology. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Blood chemistry of B-hCCR8 mice
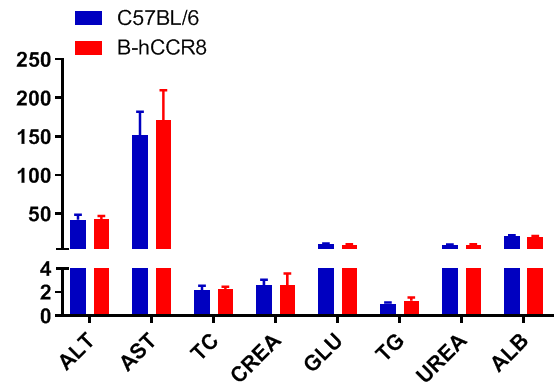
Blood chemistry tests of B-hCCR8 mice. Serum from the C57BL/6 and B-hCCR8 mice (n=8, 9 week-old) was collected and analyzed for levels of indicators. The measurements of B-hCCR8 mice were similar to that in C57BL/6 mice, indicating that humanization does not change the health of related tissues, such as liver. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacious of anti-human CCR8 antibody
In vivo efficacy of anti-human CCR8 antibody
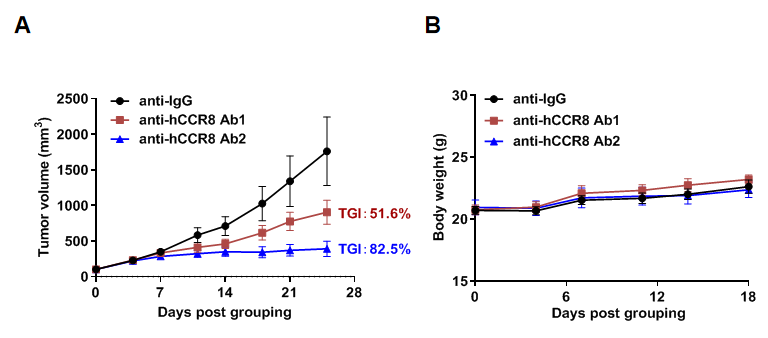
Antitumor activity of anti-human CCR8 antibody in B-hCCR8 mice bearing MC38 cells. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hCCR8 mice (female, 7 week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human CCR8 antibodies (in house). (A) Tumor growth curve. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown, anti-human CCR8 antibodies were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hCCR8 mice. B-hCCR8 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human CCR8 antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
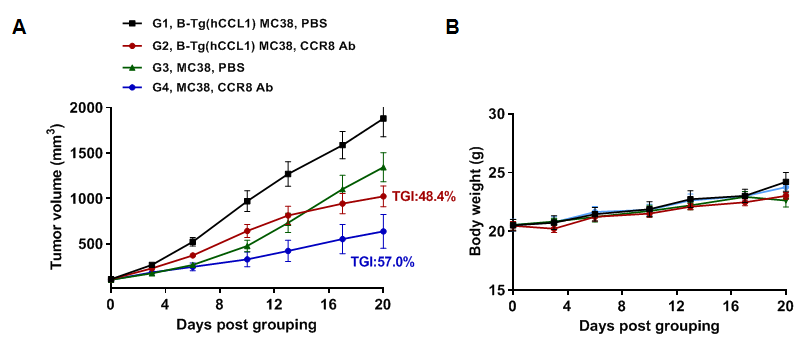
Antitumor activity of anti-human CCR8 antibody in B-hCCR8 mice. (A) Anti-human CCR8 antibody get from cooperation company inhibited MC38 tumor growth in B-hCCR8 mice. Murine colon cancer MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hCCR8 mice (female, 8 week-old, n=7). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3, at which time they were treated with anti-human CCR8 antibody. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-human CCR8 antibody were efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hCCR8 mice. B-hCCR8 mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human CCR8 antibody. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Tumor infiltrates lymphocytes analysis
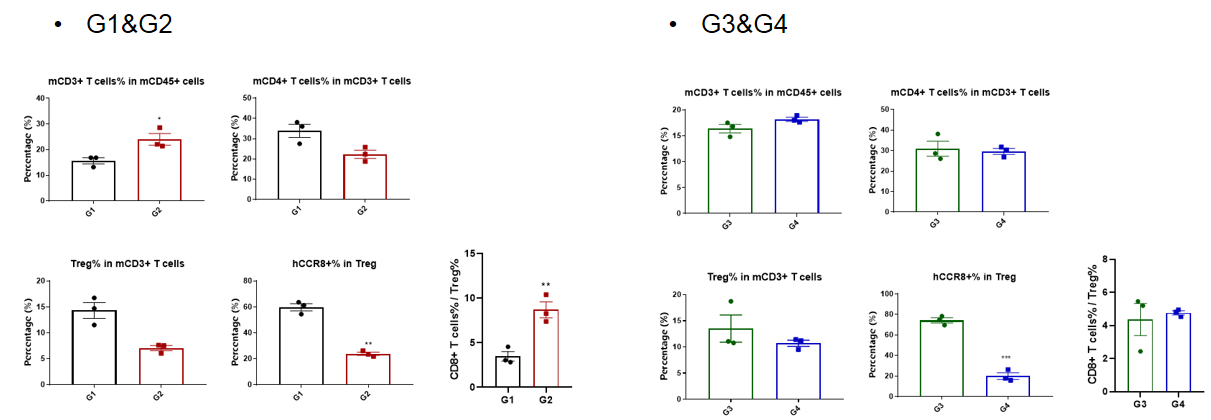
Analysis of tumor infiltrates lymphocytes by FACS.TILs were harvested at the endpoint of the experiment and flow cytometry analysis was performed to assess the leukocyte subpopulations. The percent of CCR8+ Treg cells were significant decrease in anti-human CCR8 antibody treatment group (G2, G4), and the ratio CD8+ T cells to Treg cells increased significantly in G2, but not in G4. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001)































 京公網安備: 11011502005564號
京公網安備: 11011502005564號