B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice
| Strain Name |
C57BL/6-Pdcd1tm1(PDCD1)Bcgen Cd274tm1(CD274)Bcgen Vegfatm1(VEGFA)Bcgen /Bcgen
|
Common Name | B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 112706 |
|
Related Genes |
CD279, PD-1, PD1, SLEB2, hPD-1, hPD-l, hSLE1; B7-H, B7H1, PD-L1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, PDL1, hPD-L1; MVCD1, VEGF, VPF |
||
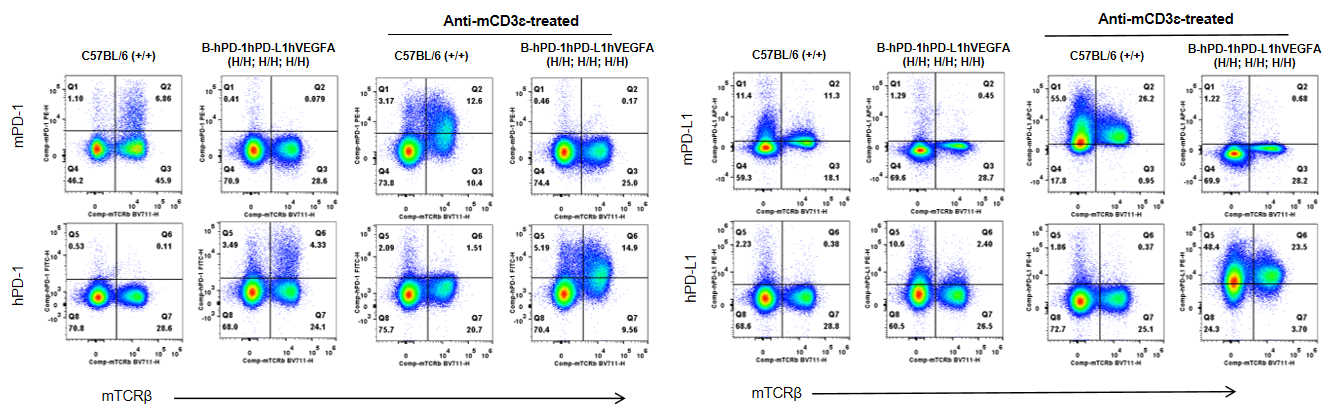
Strain specific PD-1 and PD-L1 expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6 and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice (H/H; H/H; H/H) after stimulated with or without anti-CD3ε in vivo. Mouse PD-1 and PD-L1 were detectable in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Human PD-1 and PD-L1 were exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice but not in wild-type mice.
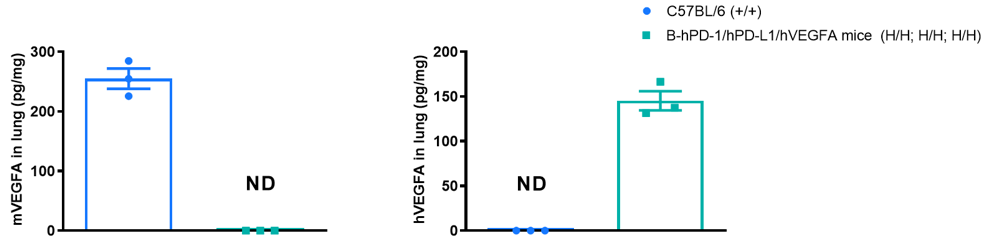
Strain specific VEGFA expression analysis in wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice by ELISA. Lung homogenates were collected from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice (H/H; H/H; H/H). Mouse VEGFA was detectable in wild-type mice. Human VEGFA was exclusively detectable in homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice, but not in wild-type mice.

Frequency of leukocyte subpopulations in spleen by flow cytometry. Splenocytes were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice and homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice (n=3, 10-week-old). A. Flow cytometry analysis of the splenocytes was performed to assess the frequency of leukocyte subpopulations. B. Frequency of T cell subpopulations. Percentages of T cells, B cells, NK cells, dendritic cells, granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and Tregs in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice were similar to those in C57BL/6 mice, demonstrating that humanization of PD-1, PD-L1 and VEGFA does not change the frequency or distribution of these cell types in spleen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.

Antitumor activity of anti-PD-1/VEGFA bispecific antibody (ivonescimab analog, in-house) in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice. (A) Anti-PD-1/VEGFA bispecific antibody inhibited B-hVEGFA MC38 tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice. Murine colon cancer B-hVEGFA MC38 cells were subcutaneously implanted into homozygous B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice (female, 8-week-old, n=6). Mice were grouped when tumor volume reached approximately 70-90 mm3, at which time they were intraperitoneally injected with anti-PD-1/VEGFA bispecific antibody indicated in panel. (B) Body weight changes during treatment. As shown in panel A, anti-PD-1/VEGFA bispecific antibody was efficacious in controlling tumor growth in B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice, demonstrating that the B-hPD-1/hPD-L1/hVEGFA mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-PD-1/VEGFA bispecific antibodies. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Significance was determined by two-way ANOVA test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
The overage of this tumor model is 50%.










 京公網安備: 11011502005564號
京公網安備: 11011502005564號