| Strain name | Non-disclosure | Common Name | B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus |
| Background | C57BL/6 | Catalog number | 112744 |
| Aliases |
TSLP: NA;CRLF2: CRL2Y, TSLPR |
||
Protein expression analysis-TSLP

Strain specific TSLP expression analysis in wild type C57BL/6 mice, homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus by ELISA. Calcipotriol (MC903) was dissolved in ethanol and topically applied on ears of wild type C57BL/6 mice, homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus for 7 days. Ear grinding supernatant from the three strain of mice were analyzed by ELISA. Mouse TSLP was only detectable in wild type C57BL/6 mice. Human TSLP was detectable in homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus but not in wild type mice.
Detection of longer and shorter isoform expression of human TSLP by RT-PCR
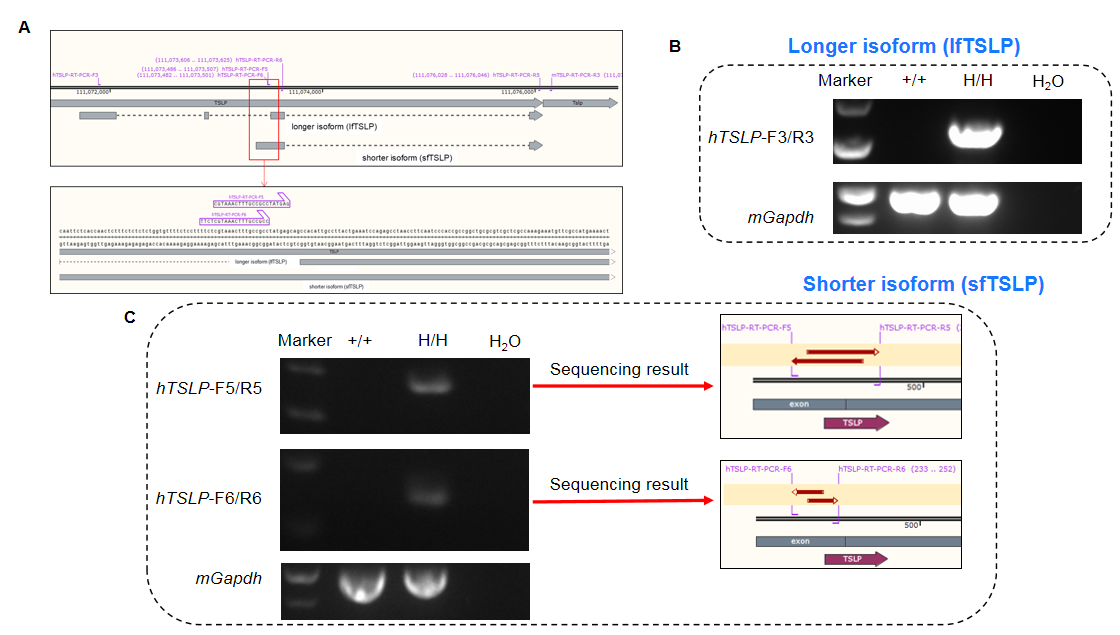
Longer and shorter isoform of human TSLP were detectable in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus by RT-PCR and sequencing. Ear tissues were isolated from wild-type C57BL/6 mice (+/+) and homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus (H/H). A. Primers were designed to detect longer isoform (lfTSLP) and shorter isoform (sfTSLP) of human TSLP; B. LfTSLP mRNA was detectable in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus, but not in wild-type mice; C. SfTSLP mRNA was detectable in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus, but not in wild-type mice. The sequencing results of the shorter isoform PCR products confirmed that the sequences amplified in mice were consistent with those in the database.
Protein expression analysis of TSLPR in spleen

Data from Huabo Biopharm Co. Ltd.
Mouse and human TSLPR expression analysis in splenocytes. Splenocytes were collected from wild type C57BL/6 mice, homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. TSLPR expressed on cDC, pDC and non DCs were analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TSLPR antibody. Mouse TSLPR were detectable on cDC, pDC and non DCs of wild type C57BL/6 mice, but not on the cells of TSLPR humanized mice. Human TSLPR was detectable on cDC, pDC and non DCs of B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus, but not on the cells of wild type C57BL/6 mice.

Data from Huabo Biopharm Co. Ltd.
Mouse and human TSLPR expression analysis in bone marrow. Bone marrow cells were collected from wild type C57BL/6 mice, homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. TSLPR expressed on bone marrow cells were analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific anti-TSLPR antibody. Mouse TSLPR were detectable on cDC, pDC and non DCs in wild type C57BL/6 mice, but not on the cells of TSLPR humanized mice. Human TSLPR was detectable on cDC, pDC and non DCs of B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus, but not on the cells of wild type C57BL/6 mice.
Protein expression analysis of hTSLPR in cDC1 from bone marrow

Data from Huabo Biopharm Co. Ltd.
Human TSLPR expression analysis in cDC1 from bone marrow. Bone marrow were collected from wild type C57BL/6 mice, homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. Human TSLPR expressed on cDC1 were analyzed by flow cytometry with species-specific antibodies. Human TSLPR was highly expressed on the cDC1 in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus.
Analysis of leukocytes cell subpopulation in spleen









Data from Huabo Biopharm Co. Ltd.
Mouse TARC was respectively induced with human TSLP and mouse TSLP in wild type C57BL/6 mice, homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. Dendritic cells were respectively induced with FLT3L from bone marrow of the three strains and stimulated with human TSLP or mouse TSLP in vitro. Concentration of mouse TARC secreted from DCs was assayed by ELISA. Mouse TARC was successfully induced with human TSLP, but not mouse TSLP in homozygous B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. The level of mTARC in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus was higher than that in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. Meanwhile mouse TARC was successfully induced with mouse TSLP, but not human TSLP in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Results indicated that TSLP and TSLPR are not cross-reactive between mouse and human. Human TSLP can activate the dendritic cells of B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus.
Growth curve


Complete blood count (CBC) of B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.

Blood biochemical test of B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. Values are expressed as mean ± SD.

The organs of female B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus (12-week-old, n=10).

The organs of male B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus (12-week-old, n=10).

Average weight of the main organs of B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus.

In vivo efficacy of anti-human TSLP antibody in a new mouse asthma model

Analysis of inflammatory cells in BALF by FACS. Mouse asthma model was induced in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice and treated with anti-human TSLP antibody (tezepelumab, synthesized in house). BALF was collected at the end of the experiment to detect infiltrated inflammatory cells in lung tissue. The results showed that CD45+ cells, eosinophils and neutrophils in the group (G2) treated with anti-human TSLP antibody decreased significantly when compared with the group (G1) treated with isotype antibody. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
In vivo efficacy of anti-human TSLP antibody in a new mouse asthma model

OVA specific IgE in serum and TARC in BALF were significantly reduced in the mouse asthma model treated with anti-TSLP antibody. Serum was collected at the study endpoint. IgE and TARC levels were analyzed by ELISA. The results showed that the levels of OVA specific IgE and TARC in mice treated with tezepelumab (in house) was lower than that in untreated mice. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. TARC: thymic and activating regulatory chemokine, also known as CCL17 (C-C motif chemokine ligand 17).

H&E staining of asthma-like model in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. Lung tissues were collected at the study endpoint and analyzed with H&E staining. The results showed that compared to the untreated group (G1), the group of mice treated with tezepelumab (in house) showed a significant reduction in inflammatory infiltration and mucus secretion in lung tissue, indicating that B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human TSLP antibodies. Black arrow: inflammatory cells; black triangle: eosinophils; asterisk: mucus. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
Experimental schedule for Induction of AD-like skin lesions and in vivo efficacy of anti-human TSLP antibody

Experimental schedule for Induction of atopic dermatitis (AD)-like skin lesions and in vivo efficacy of anti-human TSLP antibody in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. OXA was applied to ear skin of mice on day 0, and then challenge to the same site of skin nine times from days 7 to 25. Anti-human TSLP antibody tezepelumab (in house) was administered by intraperitoneal injection (n = 6). OXA: oxazolone.

Efficacy of anti-human TSLP antibody in B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus. Mice in each group were treated with anti-hTSLP antibody tezepelumab (in house). (A) Statistical analysis of ear thickness in each group. Epidermis of ear began to desquamate from day 18. So the ear thicknesses were decreased from day 18 as shown in figure. (B) Body weight changes during the treatment. (C) Total IgE levels in serum. Serum was collected on day 26 and total IgE levels were measured by ELISA. (n = 6). Values are expressed as mean ± SEM.
H&E staining of ear skin in AD-like mouse model of B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus

Effects of anti-human TSLP antibody on ear skin of the AD mouse model.(A) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. (B) Thickness of ear epidermal skin. (C) Score of eosinophils infiltrated in ear epidermal skin.(D) Total score of ear epidermal skin. Ear thickness and infiltration scores of eosinophils in ear skin of the groups treated with Tezepelumab (in house) were decreased significantly compared to that in the isotype control, demonstrating that the B-hTSLP/hTSLPR mice plus provide a powerful preclinical model for in vivo evaluation of anti-human TSLP antibodies. Infiltration score of eosinophils: 1=slight; 2=mild; 3=moderate; 4=severe. The content of the pathology total score evaluation includes the following aspects: epidermal hyperplasia in skin, erosion/crusting, hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis; inflammatory cell infiltration in dermis and subcutaneous. AD: Atopic dermatitis.










 京公網安備: 11011502005564號
京公網安備: 11011502005564號